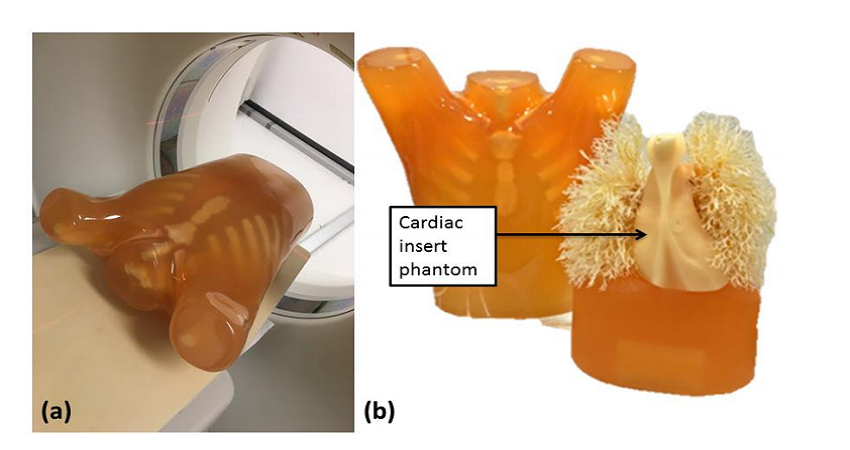
Researchers from University of Sydney, including Kamarul Amin Abdullah, performed a three-tiered study that included: 3D printing a cardiac insert phantom created from volumetric CT image datasets, investigating the 3D printed phantom in evaluation an IR algorithm and evaluating optimal IR algorithm strengths for low-tube voltage CCTA protocols. They came up with the Lungman anthropomorphic chest phantom which is equipped with a phantom that mimics the heart, and the insert was created on a Creatbot DM Plus 3D printer. They also discovered that 3D printing was suitable for dose optimization studies, allowing for investigation of IR algorithm on dose reduction.