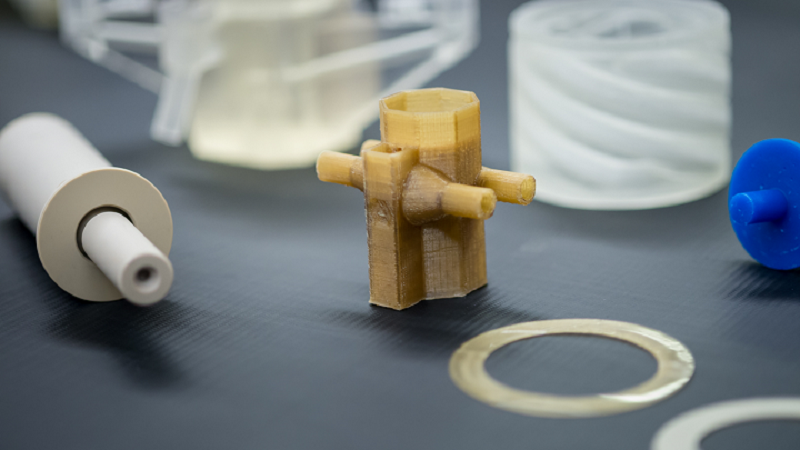
Molybdenum or Mo-99 decays into technetium-99m, which is then used to detect bone decay, heart disease, and rare cancers,but costs roughly $1,000 per gram. A team of Researchers from DOE’s Argonne National Laboratory have successfully developed the recylcing process of Molybdenum using 3D printed acrylic contactors. To counteract the corrosion of contractors by acids used in recycling process, they turned to polyetheretherketone, or PEEK, which is more durable than the original acrylic plastic they were using, and also resists the Argonne recycling method’s organic solvents and mineral acids.
 Medical 3D Printing & Bioprinting
Medical 3D Printing & Bioprinting